Table of Contents
What is collagen?
Collagen is the most prominent protein in your body and is found in your skin, muscles and bones. It holds your body together and keeps it strong, making sure your structure is intact.
Collagen is also responsible for your skin, keeping it looking supple and youthful. A loss of collagen starts to show with time on your facial skin, hair and even in the form of brittle nails.
Where does collagen come from?
Your body produces collagen naturally, known as endogenous collagen, which depletes as you get older. On the other hand, exogenous collagen is synthetic and comes from outside sources—this is the kind you find in common supplements and can be of marine or poultry origin.
Vegan or vegetarian collagen is a blend of nutrients that can boost your body’s natural collagen production capabilities. There is no vegetarian source of synthetic collagen that can be consumed, unfortunately.
What does collagen do?
Collagen is responsible for your skin, bones and connective tissues, making sure your body functions well physically and your structure is strong. It makes up 1/3rd of your body and also keeps elasticity intact and boosts cell rejuvenation.
Collagen for medical treatment
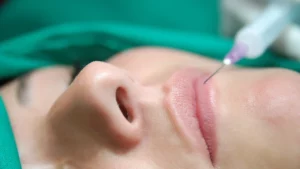
Collagen can be injected into your skin to increase your cell turnover rate, making your skin appear younger. They can also fill in hollows in your skin and improve your skin structure like your jawline and aids in reduction of fine lines and wrinkles.
It is worth noting that injected collagen works on filling in the superficial layers of your skin. The kind of collagen that is used for this comes from humans, pigs, cows or sheep. However, we do not inject collagen nor do we recommend it due to severe risks associated with collagen injections.
Nutrients that increase collagen naturally
Including certain nutrients and foods in your diet can help boost collagen production at least to a certain degree.
Proline found in egg whites, cheese, meats and soy, anthocyanidins in berries such as blueberries, blackberries, raspberries and cherries, Vitamin C from oranges and strawberries, Vitamin
A from animal-based foods and plant-based foods rich in beta-carotene and copper, which is usually found in red meat, nuts and shellfish and also drinking water if you store your water in a copper bottle for hours. Consuming these foods regularly can help boost loss of collagen over time.
How to prevent loss of collagen
Apart from consuming the aforementioned foods in your diet, it’s essential that you make sure that you follow a healthy lifestyle, with adequate sleep, a balanced diet and minimal sun exposure (even with sun protection) to prevent this collagen damage.
Cutting out processed foods, excessive high GI carbs and sugar can all help keep your skin’s collagen quality and levels in tact for longer. Always, always wear sunscreen, include antioxidants in your skincare and consume foods rich in the same and sign up for the right treatments at your dermatologist’s clinic to keep your collagen working in your favour for longer.
All the ways natural collagen can be damaged
While your body’s natural ability to produce collagen reduces over the years due to age, it can start to reduce sooner than you’d like as well. Not getting enough sleep, an erratic lifestyle, smoking, a high-sugar diet and UV exposure can damage existing collagen at a faster rate than it normally would deplete.
When you consciously think about it, each of these reasons can be avoided by focusing more on what you consume, what your everyday life looks like and how often you take to tobacco, if that is your vice.
Collagen supplements

Should you take them?
Collagen supplements are synthetic sources of collagen derived from marine and bovine animals to increase collagen in your body, aiding healing, skin cell rejuvenation and looking after depleting levels.
If you’re noticing signs of aging cropping up on your skin, weaker hair and nails, it could be worth it to give a daily collagen supplement a shot. Regular use has shown significantly promising results for people across the globe.
Do they work?
Collagen supplements are available in the form of liquids, powders and pills. The liquid and powder forms are the most effective of the three in improving existing collagen levels and aiding better future production.
It’s important to note that vegetarian and vegan collagen supplements can only help accelerate your body’s own collagen production, they do not introduce any synthetic versions when consumed. Marine collagen is the most effective to improve the quality of your skin.
When trying a supplement wherein bovine animals are the source of collagen, it’s worth it to check the source of the synthetic collagen to ensure its pure and not derived from animals that have been chemically-induced.
Benefits
- They’re a fairly easy way to increase collagen levels and improve the condition of your skin.
- Collagen supplements are now also available in flavours such as chocolate, vanilla and berries, making them convenient to consume as part of your daily routine.
- These supplements can also help relieve joint pain and prevent your bones from getting weak.
- Collagen supplements often come with a blend of additional nutrients, all when consumed together can have a positive impact on the quality of your skin, hair and nails.
- The collagen found in supplements is already hydrolyzed meaning it has been broken down using water, making it easy to absorb as opposed to trying to increase your levels through dietary changes.
Possible side effects
Collagen as such does not have any side effects, when injected or consumed in the form of a supplement. The only side effect you can possibly notice is an allergic reaction to the source of the collagen.
Whether marine, bovine or vegetarian, look into the actual source of the collagen and check for any allergy markers before you start to consume them. Collagen supplements can rarely also cause some acne.
Collagen creams
Collagen creams tend to be more of a marketing gimmick as opposed to a truly effective product.
These products do not actually contain collagen in them—they are intensely moisturising in most cases and any improvement you notice on the surface of the skin is due to other ingredients in the cream. None of these creams can directly increase collagen production.